Python Course Nontapat Thaiprayoon
Resources
Download:
Code in Class:
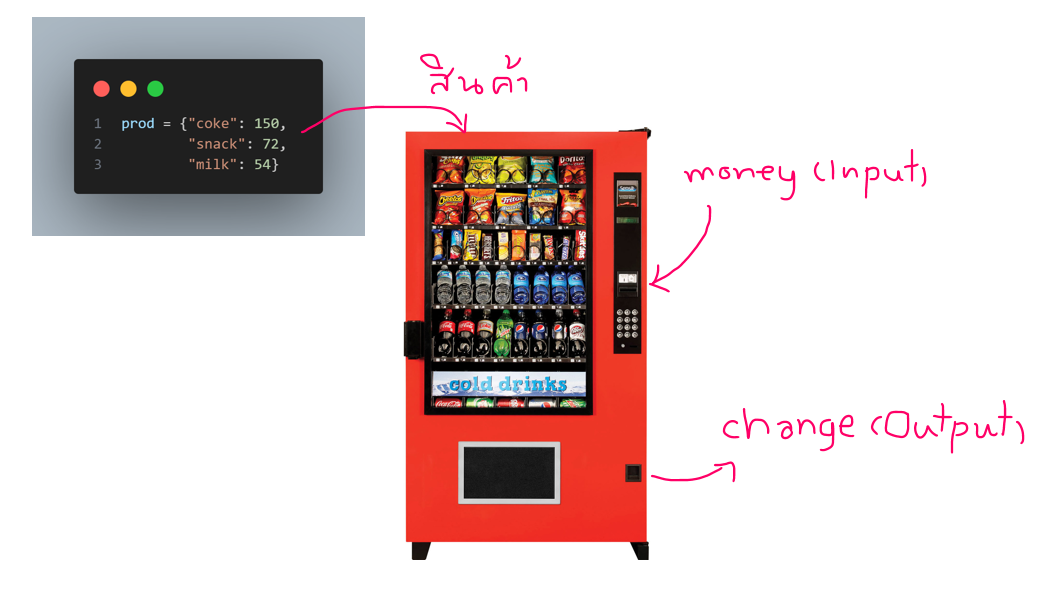
Vending Machine
x = [1000, 500, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 1]
prod = {"coke": 150, "snack": 72, "milk": 54}
def cal_money(money, product):
prod2 = prod[product]
change_money = money - prod2
print(f"change_money : {change_money}")
for i in x:
money2 = change_money // i
print(f"{i} :", money2)
change_money = change_money % i # money %= i
cal_money(money = 8500 , product= "coke")
Class 15 Jul 2024
# value = 'a' # or 'b' or 'c'
# x = 10
# result = {
# 'a': lambda x: x * 5,
# 'b': lambda x: x + 7,
# 'c': lambda x: x - 2
# }[value](x)
# print(result)
# x = [1,2,3]
# print(x[0].__doc__)
# name = "Jane"
# age = 25
# money = 108.123
# text = "hello, %s , You are %s years old" % (name, age)
# print(text)
# text = "hello, {} , You are {} years old".format(name, age)
# print(text)
# text = f"hello, {name} , You are {age} years old"
# print(text)
# text = f"Blance: {money:.2f}"
# print(text)
# Dictionaries
# my_set = {1,2,3}
# my_dict = {"A": [1,3,4],
# "B": 2, "C": 3}
# print(type(my_dict))
# print(my_dict["A"][2])
# for i in my_dict.values():
# print(i)
# ==============================================
# Switch
# value = 'b'
# x = 10
# result = {'a': lambda x: x * 5,
# 'b': lambda x: x + 7,
# 'c': lambda x: x - 2}[value](x)
# print(result)
# ==============================================
# List Comprehension
# fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
# newlist = []
# # for x in fruits:
# # if "a" in x:
# # newlist.append(x)
# newlist = [x for x in fruits if "a" in x]
# print(newlist)
# OOP object oriented programming
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def display_name(self):
print(self.name, "is employee name")
# a49_1 = Person(name = "LL", age = 15)
a49_1 = Person("LL",15)
print(a49_1.name)
print(a49_1.age)
a49_1.display_name()
Class 11 Jul 2024
# Conditions
# True, False
# x = 1
# y = 2
# print(x == y) # equals
# print(x != y) # not equals
# and , or
# name = "Lawrence"
# age = 18
# if name == "Nonny" and age == 19:
# print("OK")
# name = "Nonny"
# age = 18
# if name == "Nonny":
# name = "LL"
# print("A")
# elif name == "Lawrence":
# print("B")
# elif name == "Bow":
# print("C")
# else:
# print("else")
# print(name)
# # List
# list_name = ["Nonny", "Lawrence", "Bow"]
# #Tuple
# tuple_name = ("Nonny", "Lawrence", "Bow")
# #Set
# my_set = {"Nonny", "Lawrence", "Bow"}
# if "Nonny" in list_name:
# print("YES")
# else:
# print("NO")
# Loops
# while loops
# number = 1
# while number < 10:
# print("OK : ", number)
# number = number + 1 # number += 1
# if number == 5:
# break
# for loops
# list_fruits = ['apple', 'banana','cherry']
# for i in list_fruits:
# i = i + " ff"
# print(i)
# print(i)
# [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
# list_01 = []
# for i in "Pongsakorn":
# list_01.append(i)
# print(list_01)
# print(list_01)
# name = "Pongsakorn"
# print(name)
# name[0] = "W"
# print(name)
# adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
# fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# for x in adj:
# for y in fruits:
# if y == "banana":
# print("bananie")
# print(x, y)
#=============================================
# ll = ("red", "big", "tasty")
# ll.append(12)
# ll = ("red", "big", "tasty")
# print(ll)
# ll = ll + (12,)
# print(ll)
# print(type((12)))
#=============================================
# Function
# def func01(name = "Laulen", age = 16):
# # global sentence
# sentence = "Hello %s, age = %d " % (name,age)
# print(sentence)
# func01("Bow", 18)
# fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# def my_function(food):
# for i in food:
# if i == "banana":
# print("BANANA")
# else:
# print("NOT BANANA")
# my_function(fruits)
# def my_function(x):
# y = 5 * x
# return y
# print(my_function(5))
# Lambda Function
# lambda arguments : expression
# x = lambda a : a + 10
# print(x(5))
# =============================
# def func02(a):
# x = a + 10
# return x
# print(func02(5))
# =============================
Class 8 Jul 2024
# print("Hello Worlds!")
# Numbers
# luaren love ..
# Numbers
# Integers. Float
# mynumber = 7
# print(type(mynumber))
# mynumber2 = 7.2
# print(type(mynumber2))
# String
# mystring = 'seven'
# print(type(mystring))
# mynumber = 7 - 2.1
# print(mynumber)
# x = 686846886
# ll = "laulen" + " " + "3=49t=349t=3t_*^%+" + str(x)
# print(ll)
# nn, ll = 7, 3
# print(ll)
# pun = 7
# ll = 3
# nn = ll + 2
# print(nn)
# pun = 12
# Pun = 7
# print(Pun)
# Basic Operators
# print(5 + 6) # addition
# print(6-5) # subtraction
# print(6*5) # multiplication
# print(6/5) # division
# print(7 % 5) # modulus
# print(2 % 2)
# print(10 % 3)
# print(11 % 2)
# print(2 ** 2) # exponentiation
# print(4 == 1) # eqaul to
# Boolean = True, False
# print(4 != 4) # not eqaul to
# print(6 > 4) # greater than
# print(6 < 4) # less than
# print((1 + 2) * 3 / 4.0)
# 2 * 3 = 6
# 6 / 4.0 = 1.5
# 1.5 + 1 = 2.5
# ll = "laulen"
# print(ll+ " nonny")
# name = "John"
# name2 = "nonny"
# print("Hello," + name)
# print("Hello,%s" % name2)
# name = "John"
# age = 27
# print(name + " is " + str(age) + " years old")
# print("%s is %d years old." % (name, age))
# List
# my_list = ["LL", 2 , "LL" ,True, None]
# print(type(my_list))
# print(type(my_list[-1]))
# my_list.append("Bov")
# my_list.append("Sert")
# my_list.insert(1, "nonny")
# my_list.remove("LL")
# my_list.pop(0)
# print(my_list.count(2))
# my_list = ["LL", 2 , "LL" ,True, None]
# my_list[0] = "nonny"
# print(my_list)
# Tuple
# my_tuple = ("nonny", "LL", 12)
# my_tuple[0] = "Bov" # TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
# print(my_tuple)
# my_set = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
# my_list = ["LL", [1, 12, 15], ("nonny", 12)]
# print(my_list[2][1])
# Sets
# my_set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
# my_set2 = {1, 2, 3}
# my_set3 = my_set1.union(my_set2)
# print(my_set3)
# {'banana', 1, 2, 3, 'cherry', 'apple'}
# {1, 2, 3, 'cherry', 'banana', 'apple'}
# set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
# set2 = {"google", "microsoft", "apple"}
# set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
# print(set3) # {'apple'}
# set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
# set2 = {"google", "microsoft", "apple"}
# set3 = set1.difference(set2)
# # set3 = set1 - set2
# print(set3)
set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry", "apple"}
print(set1)
BMI
def BMI(weight, height):
# bmi = ...
bmi = weight / (height / 100) ** 2
# 1 condition # thin
if bmi < 18.5:
category = "Thin"
# 2 condition # normal
elif 18.5 <= bmi < 24.8:
category = "Normal"
# 3 condition # overwuight
elif 25 <= bmi < 29.9:
category = "Overwuight"
# 4 condition # obese
else:
category = "Obese"
return "You are %s" % category
print(BMI(80, 180))
pack py
# pack.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Circle:
"""
The class Circle has the attribute redius and color.
"""
# Constructor
def __init__(self, radius = 3, color = 'blue'):
self.radius = radius
self.color = color
# Method 1
def add_radius(self, r):
self.radius = self.radius + r
return(self.radius)
# Method 2
def drawCircle(self):
plt.gca().add_patch(plt.Circle((0, 0), radius=self.radius, fc=self.color))
plt.axis('scaled')
plt.show()
main py
# main.py
# import pack
from pack import Circle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# from pack import *
red_circle = Circle(10, "red")
# print(red_circle.__doc__)
red_circle.drawCircle()